The rise of ghost kitchens was prominent during the COVID lockdown because people could not dine out and struggled to buy groceries. For the uninitiated, ghost kitchens are delivery-only food establishments. Regular restaurants have a logistics and food preparation backend and a service frontend that is visible to customers. Meanwhile, ghost kitchens don’t have a service frontend and operate in the shadows, giving birth to the ‘dark kitchen’ moniker.
Of course, ghost kitchens existed before the pandemic; however, they were not quite popular. As the pandemic kept millions of people indoors, the rise of ghost kitchens became glaring.
The burning question is whether this ghost kitchen business model will go the long haul or soon lose relevance. Let’s analyse the precedents together and consider potential outcomes.
What Are Ghost Kitchens?
Ghost kitchens are establishments designed exclusively for delivery orders. Customers don’t need to visit a mortar and brick restaurant. The ghost kitchen business model has been touted as the future of restaurant industry.
From an entrepreneur’s perspective, you can start a food brand without the hassle of setting up a kitchen. Such food brands can strike up contracts with multiple food-delivery kitchens to meet customer orders. For example, viral YouTuber Jimmy Donaldson, also known as Mr Beast, created a food brand, MrBeast Burger, in 2020.

The foremost incentive for businesses hopping on virtual restaurant trends is that they seldom have to invest in setting up an actual kitchen. For example, MrBeast Burger signed an agreement with Virtual Dining Concepts as its ghost kitchen partner.
Ghost kitchen marketing strategies make it way cheaper to operate a food business. For example, no dine-in or seating infrastructure, decór or waitstaff is needed. Also, these cloud kitchen concepts have taken marketing for dark kitchen brands to new heights. So, unlike conventional restaurants that run ads and woo customers by every means possible, ghost kitchens’ marketing strategies exploit digital platforms like social media and apps for publicity.
ALSO READ: How AI Is Changing the Way We Order Food
The Appeal of Ghost Kitchens
From the perspective of a food entrepreneur, the rise of ghost kitchens showed rays of hope as a good business model. Enthusiasts of innovations see ghost kitchens as the future of restaurant industry.
Let’s brush through some merits that recently earned ghost kitchens billions of dollars in venture capital:
1. Cost Efficiency
Food business leaders have found food delivery-only kitchens to be cost-effective relative to conventional restaurants. Since ghost kitchens can share facilities and don’t need to invest in dining areas, they can cut down the unit price of each food serving. Consequently, the digital dining trends afford ghost kitchens some level of comparative advantage through cheaper prices. Naturally, higher traffic driven by consumers looking for better deals could lead to a more profitable ghost kitchen business model.
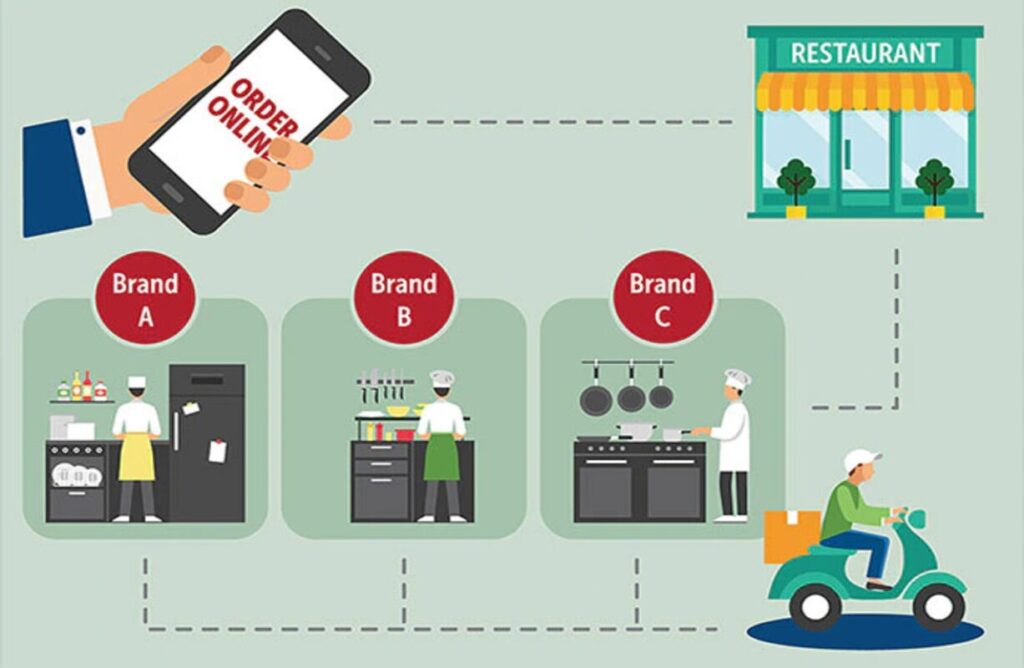
2. Business Scalability and Adaptability
Adopting cloud kitchen concepts into the restaurant business allows brands to innovate seamlessly. For example, ghost kitchens can iterate and try out different menus without necessarily altering their restaurant space. In addition, virtual restaurant trends also make it possible for chefs to be adventurous with fusion cuisines and with minimal risk to the ghost kitchen.
3. Lean Operations
Managing the dining hall of conventional restaurants is one of the most taxing aspects of the business. Its direct link to the restaurant’s PR forces management to strive to leave a positive impression on customers. Ghost kitchens often outsource food delivery to third-party companies. So, the headache of delivery logistics goes off their plates. Indeed, you can maintain the barest minimum of workforce and even automate processes where possible.
Key Technologies Powering Ghost Kitchens
The rise of ghost kitchens was made possible by the intersection of multiple pivotal technologies. Some, if not all, of these technologies were not available, or in full bloom, in the 20th century. Inferentially, ghost kitchens would have been impractical in the said period.
Now, a quick rundown of the technologies serving as the backbone for the rise of ghost kitchens:
- Third-party delivery platforms
- AI-driven order optimization
- Advanced data analytics

There would be no ghost kitchens without the three technologies listed above. Advanced data analytics help ghost kitchens streamline menus and marketing campaigns to fit the preferences of each customer. Also, predictive analytics makes it possible to preempt variations in seasonal demand. Big data collected from digital dining trends could help ghost kitchens optimize the stocking and utilization of resources.
Ghost kitchens rely heavily on AI-driven order management systems. If a high-traffic ghost kitchen handles orders manually, it is bound to run into disaster. So, order optimization using AI makes understanding ghost kitchens and matching up logistics to incoming orders possible. In some cases, it may help management identify the need to expand and promptly attend to the stream of orders as the kitchen’s brand gains a foothold.
Finally, third-party delivery platforms are an essential backbone of ghost kitchen operations. These platforms handle the logistics of getting the prepared meal from a ghost kitchen to the customer in the shortest time possible. Indeed, the quality of this aspect of the ghost kitchen business can make or mar brand credibility. For example, MrBeast Burger sued Virtual Dining Concept for negative feedback from brand customers. Some of the complaints were about the promptness of order delivery.
ALSO READ: The Future of Food: What Will We Be Eating in 2050?
Challenges Faced by Ghost Kitchens
One of the prominent challenges facing the ghost kitchen business model is competition. Traditional restaurants are unforgiving of the pilfering of their customers. So, some of these restaurant chains are hopping on the virtual restaurant trend. For example, the owners of the Chilli’s restaurant, Brinker International, started two ghost kitchen concerns in 2020. They called the two new entrants Maggiano’s Italian Classics and It’s Just Wings. However, by 2023, Brinker had to shut down Maggiano’s and scale down on It’s Just Wings. The problem? Folks went back to in-person dining after lockdown restrictions were lifted.
The ghost kitchen business model is still virgin ground and may not yield profits as expected. Consequently, startups should heed some caution. Meanwhile, established restaurant chains can proceed with investments in ghost kitchens, even if they operate at a loss. These big-timers can easily recoup their losses from other businesses and simultaneously win turf and customer loyalty for a time when the ghost kitchen market would become profitable.

Another challenge facing ghost kitchens is food quality retention during delivery. If a ghost kitchen is unable to find suitable third-party delivery companies to fulfil customer orders, it may have to do the delivery itself. There is more to the quality of food delivery services than just getting the meal to the customers’ doorstep before the deadline. So, the third-party delivery platform must integrate the ghost kitchen’s culture into its services.
The Future of Ghost Kitchens
Since the rise of ghost kitchens during the pandemic, investors have had a bitter-sweet experience. Many, like Brinker International, are having second thoughts. Well, the eventual decision of where the investment should go lies with venture capitalists. However, certain virtual restaurant trends may help the ghost kitchen business model gain a strong footing shortly.
Niche Food Services
Some ghost kitchens may niche out in a bid to establish themselves as authorities in a speciality. For example, they may specialise in providing consumers with trending dishes, and some may narrow down on personalized diets (like vegan and keto).

Hybrid Ghost Kitchens
Ghost kitchens would likely arrive at a compromise about their no-dine-in policies. Some ghost kitchens may innovate by allowing small footprint seating areas, and some may use pick pods with smart lockers. Food brands in Asia are already experimenting with drone delivery to local pods.
Collaborative and Integrated Marketing
Most tech companies are massively collaborating to milk potential customers from every corner of the internet. Similarly, ghost kitchens may collaborate symbiotically with popular food brands in the future. They may even use influencers and celebrities to further their cause.
Automated Operations and Delivery
Pazzi is the first startup in the world to produce pizza autonomously using robots. The food industry already boasts several automated operations in innovative facilities. However, it would not be surprising if future ghost kitchens prepare meals using autonomous robots, also becoming a selling point in their marketing campaigns.
The viability of the ghost kitchen business model may be floundering momentarily after its unprecedented rise during the pandemic. Nonetheless, we see the growth of ghost kitchens as inevitable in the future. However, we cannot tell whether ghost kitchens will dominate the food service industry or continue thriving as a niche. Let us know what you think.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Babatunde Olufemi is a food scientist, educator, and science-based food writer with academic and practical exposure to food processing, nutrition, food safety, and the global food industry. Through Quill of Grubs, he breaks down complex food science topics into clear, accessible explanations for everyday readers, students, and professionals.











