In this piece, we shall answer the question, “Is microwaving food bad?” The average kitchen in a 21st-century home or restaurant features at least one microwave oven. This is enough evidence that technology has become an integral part of our culinary habits and everyday lives. Indeed, even folks who do not have the appliance at home still consume microwaved food items passively. Indeed, microwave ovens are massive time-savers.
We need to address the elephants in the room concerning microwave cooking safety. For example, we shall address some microwave cooking myths, particularly regarding its impact on food nutrients and consumer health.
So, we shall present science-based evidence about the technology’s safety, beyond existing sentiments about microwave cooking,
How Do Microwaves Cook Food?
Answering the question, “Is microwaving food bad?” is difficult without some understanding of the technology. At the very least, the reader needs an awareness of the first principles of microwave radiation. So, here it comes.
The microwave oven is a product of serendipity. In 1945, Percy Spencer, an American engineer, worked with a magnetron when he discovered microwaves. He noticed that the equipment had melted a chocolate bar in his pocket. The magnetron was an electron tube that helped radar systems better detect enemy aircraft. Spencer was working for Raytheon, an aerospace and defense company, at the time of the discovery. He filed for a patent shortly after, and Raytheon unveiled the first commercial microwave oven, Radarange, in 1947.
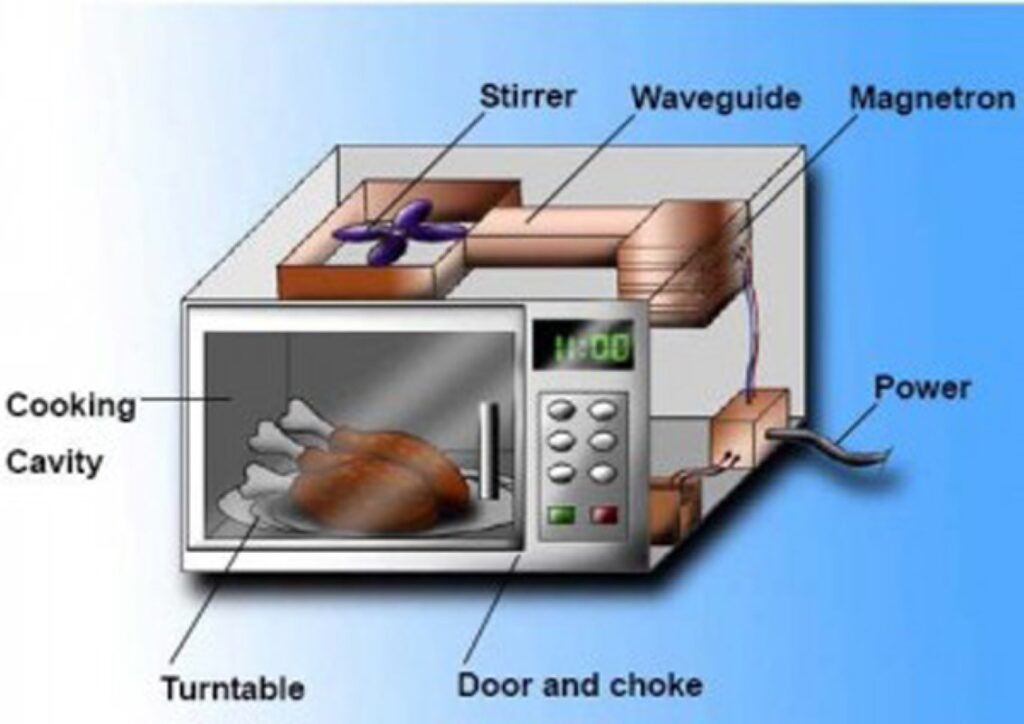
So, a microwave oven is a magnetron in a protective enclosure. The magnetron converts electrical energy into high-frequency radio waves. These electromagnetic waves are then channelled into the oven compartment, where polar food molecules like water become excited. Consequently, the excitement causes the molecules to vibrate at a similar frequency as the microwave, and the resulting friction causes the food to heat up.
ALSO READ: Are Organic Foods Really Healthier? The Truth Behind the Hype
Does Microwaving Food Reduce Nutrients?
It is a given that any form of cooking tends to reduce the nutritional content of food. So, while the straight answer to the question at the beginning of this section is “yes,” the same answer applies to frying, boiling, baking, and any other form of cooking.
Indeed, some studies suggest that nutrient loss in microwaved food is sometimes low relative to other cooking methods. For example, a couple of studies affirm that there is no difference in the rate of nutrient loss in food materials processed by microwaving and conventional cooking.

It would be unrealistic to place a hallow on microwave cooking. In some instances, it scores low on retaining some heat-sensitive food nutrients. For example, a study found that microwaving easily destroys an anti-carcinogen, sulforaphane, in broccoli. However, in most other instances, the nutrient loss in microwaved food is far lower than in boiling or pressure cooking.
Of course, the outcome of the many scientific juries that compare food microwaving to other cooking methods depends on multiple factors. For example, many of these studies consider the cooking time, temperature, and presence of oil, water and sugars in the food.
Are There Safety Risks with Microwave Cooking?
Microwave cooking safety is often the top argument of the technology’s naysayers. So, again, is microwaving food bad? Folks with sketchy knowledge about the properties of electromagnetic radiation are likely to rule out any form of radiation as unsafe. Meanwhile, radiation falls into one of two categories: ionizing and non-ionizing. The major difference between the two categories is that ionizing radiation has enough energy to dislodge electrons from their native atom. However, non-ionizing radiation merely causes electrons to vibrate in place. The implication is that ionizing radiation can alter DNA and molecular makeup of foods, while the changes that non-ionizing radiation cause are largely physical and reversible.
Examples of ionizing radiation are x-rays and gamma radiations. On the other hand, microwaves, radio waves, infrared radiation, ultraviolet radiation (UV) and visible light are all examples of non-ionizing radiation.

The question of whether nutrient loss in microwaved food was addressed earlier. Now, we shall consider some microwave safety insights. It may be unsafe to work directly with an unshielded magnetron. However, contrary to microwave radiation concerns, the modern microwave oven has several safety features that make it safe for people without technical knowledge. For example, metal shields on the glass window prevent microwave radiation from leaving the appliance. Also, most microwave oven doors are fool-proof, turning off the radiation-generating component when opened.
ALSO READ: 21 Ultra-Processed Foods to Avoid
Best Practices for Healthy Microwave Cooking
While we have established that microwave cooking is safe, there are a couple of healthy microwave practices to note. The following are highlights of some reheating food tips:
1. Avoid giving microwaved foods to minors
Microwaving baby formula or other food for minors does not alter the food composition. However, such practice may result in burns in the child’s mouth. So, the safe reheating practice that eliminates burn hazards in minors is to allow the food to cool before serving.
2. Never microwave liquids in enclosed containers
Also, avoid microwaving liquid foods beyond boiling point, particularly when such food is in an enclosed container. For example, microwaving liquid food in a bottle may result in pressure build-up and explosion of the container holding the hot liquid.
3. Preferably, Buy Microwave Ovens With a Rotating Turntable
The effect of microwave cooking may not be uniform depending on the structure and composition of your food. However, when you shop for a microwave oven with a rotating turntable, it becomes possible to achieve more uniform heating.

4. Avoid using plastic containers in a microwave oven
Only a handful of plastic types are safe for microwave ovens. Plastics not designed for microwave ovens can easily leach harmful chemicals and microplastics into your food. So, except if you are a material science expert who can easily identify these microwave-safe plastics, we recommend avoiding plastics in microwave ovens altogether. Alternatively, you can use ceramics, glass, reusable silicone or stainless steel.
5. Never try to fix a faulty microwave oven yourself
Commercial microwave oven brands scale several regulatory and standard hurdles before getting the green light for public use. If you love fiddling with gadgets and appliances, a microwave oven is one of the worst toys to pick. Tampering with the structural design of the oven may lead to radiation leakages, which can harm your health.
6. Give microwave ovens some berth
Studies recently revealed that keeping phones in your trousers pocket or under your pillow when sleeping is unhealthy. It is suggested that long-term exposure to the radio waves from smartphones could pose health risks. However, the study does not say that smartphone use is unsafe. Similarly, microwave radiation is a non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation, just like the radio waves emissions from mobile devices. So, caution your kids from pressing their faces against the microwave window by sheer inquisitiveness or in anticipation of a hot and sumptuous meal.
Is microwaving food bad? By now, we reckon you can confidently answer that question. We have established that microwave ovens are generally safe when used correctly. Simply follow our reheating food tips and healthy microwave practices. Conclusively, the science of microwaving food suggests that the technology preserves more nutrients than other harsh cooking methods.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Babatunde Olufemi is a food scientist, educator, and science-based food writer with academic and practical exposure to food processing, nutrition, food safety, and the global food industry. Through Quill of Grubs, he breaks down complex food science topics into clear, accessible explanations for everyday readers, students, and professionals.