Your next favorite snack may not be the culmination of a chef’s entire brainpower; it may be a product of human synergy with AI in food product development. Algorithms are the building blocks of artificial intelligence, and they are getting deployed in food innovation technology.
AI food industry innovation is unravelling many aspects of food manufacturing that no one thought possible a few years back. Artificial intelligence has already been used to monitor trends of commercial food consumption. However, the tempo is going a notch higher with AI-driven recipe creation. The transition time between conceptualization of food ideas and product launch has never been shorter.
Dive in to find out what the future of AI in food manufacturing would look like. This piece will start by first considering already existing AI food industry innovations, before moving on to the unknown.
How AI is Being Used in Food Product Development
It may interest you to know that AI already enjoys wide application in the food industry. So, let’s have a quick run-through of some established artificial intelligence food industry applications.
AI Flavor Prediction
Flavor prediction is one way visionaries are already deploying AI in food development. The goal is to identify consumers’ flavor preferences without explicitly asking them. Indeed, some patrons of the food industry may be unaware that they have a penchant for a flavor AI helps predict.
So, what experts do during AI flavor prediction, as studies show, is to collect big data about eating preferences. The data is often harvested from retail data, consumer review boards and even social media. Examples of already existing tools that help aggregate such a data trove into meaningful product design insights are Spoonshot and TasteWise.

Optimizing Nutritional Profiles During Food Creation
When optimizing nutritional profiles, the goal is to identify a formulation that offers the best nutritional benefits for consumers. Food scientists and engineers have been conducting optimizations before now. However, with the advent of AI, mathematical modeling, ingredient selection and processing, nutritional analysis and tracking, and similar iterations have become easy. Consequently, scientists can now work with larger food formulation data sets and produce a wider range of nutritionally acceptable food products.
Tech-Driven Food Research and Development (R&D)
Working with large data during food formulation studies may have increased error margins. However, by following the tech-driven food R&D route, the error margin is poised to drop significantly. Also, without mixing actual ingredients, AI can deploy predictive analytics to simulate thousands of formulation runs. The era of rinsing and repeating while wasting valuable resources is about to end, thanks to tech-driven food R&D.
ALSO READ: The Rise of Functional Beverages: Why Health Drinks Are Taking Over the Market
Examples of AI in Action
You’re about to have an idea of how far the food industry has come with the adoption of AI in food product development. Many people may be unaware that some food companies are actively deploying AI in their operations. So, this section will spotlight some verifiable examples of such companies.
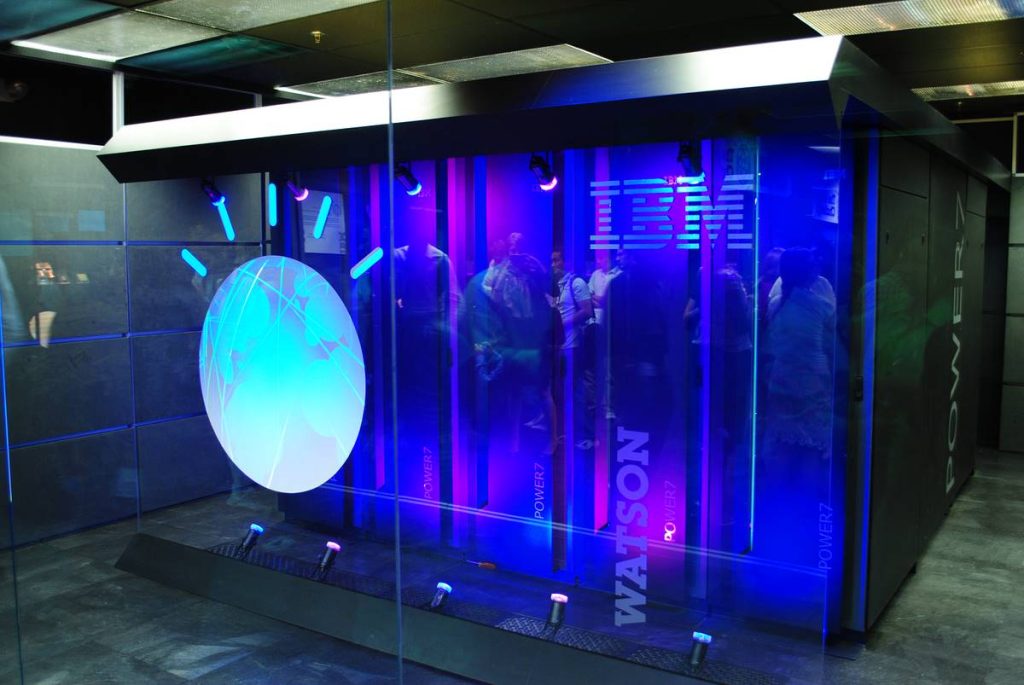
In 2006, IBM commissioned a research team, under the DeepQA project, to create a computer system that could answer questions in natural language. The project gave birth to IBM Watson, a sophisticated AI and automation system. Another moniker for the AI suite is IBM’s Chef Watson because it can, in addition to its other functionalities, help improve your cooking. Supply Chef Watson with a list of not necessarily related ingredients, and it will suggest a gourmet culinary masterpiece.

Hell Energy is a Hungarian FCMG beverage brand. In 2023, the company went viral for the ‘world’s first energy drink entirely powered by AI. All the food development activities, branding, regulatory compliance, taste evaluation, and recipe formulation for Hell Energy drink were crafted by advanced artificial intelligence.
NotCo is a Chile-based startup that is making waves by using AI in food product development. NotCo’s proprietary AI model, Giuseppe, has been able to formulate branded plant-based alternatives for animal products like meat and milk. According to Karim Pichara, NotCo’s CTO, Giuseppe is a good example of human-AI collaboration. All the company’s recipes are developed through a string of iterations between sensory experts, scientists, chefs and the AI model.
Benefits and Limitations of AI-Driven Food Innovation
A while back, the work approach of conventional R&D teams made food product formulation a nerve-racking and resource-consuming exercise. However, AI food R&D has made food product development faster and relatively cheaper. Similarly, personalizing niche products for emerging markets has also become possible. Initially, most FMCGs only determined the preferences of the largest markets for their product. Next, they would formulate a food product that fulfils the needs of their biggest customers. However, in what can be labelled as fluke marketing, the FMCGs also try to sell the generic product to small and niche markets. To avoid forcing such generic food products down the throats of customers in niche markets, AI is expediting the product personalization process.
Another merit of deploying AI in food product development is that it reduces food waste. This innovative technology cuts waste during food product development and substantive manufacturing. NotCo, for instance, claims that its AI-developed recipes make food production sustainable. For example, one of the startup’s case studies declared that its plant-based milk uses far less water, energy, and land resources relative to animal-based milk.

Some limitations of AI in food product development are listed below:
1. Data-driven recipe designs may not be what you’ll term creative
A Reddit meme summarizes this bottleneck: an AI model designs a plant-based milk recipe that is expected to supply similar doses of nutrients as the animal-based variant. However, the resulting product comes in a shade of green and tastes nothing like milk. Such challenges will force AI food R&D teams to strike a balance between technological innovation and creative ingenuity.
2. Consumer skepticism about ‘machine-made’ food
Since AI in food product development is still an emerging innovation, individuals may express reservations about trying out the products.
3. Data privacy in consumer trend analysis
Some of the machine learning models used in AI food R&D feast on sensitive consumer data. Such data could be food preferences, purchasing habits, or dietary information. There are ongoing debates about the kind of consumer data that AI models should be allowed access to, due to its security implications.
ALSO READ: What the Traditional Inuit Diet Can Teach Us About Surviving in Extreme Conditions
Future Outlook
The future of AI in food manufacturing seems bright as Big Food is already embracing its adoption. There are also prospects beyond food manufacturing, as AI is also scoring points in other areas of the food supply chain. The enhancement of supply chain optimization and sustainable sourcing of raw food materials are good examples.

Another conceptual prospect of AI in the future industry is hyper-personalization of nutrition. This has not yet gained traction in the food industry, but it may soon become possible to tailor each customer’s diet based on AI recommendations. Of course, such recommendations may be based on a combination of data about the individual’s preferences, lifestyle, microbiome, and genetic peculiarities.
However, the best innovations produced with artificial intelligence, across all industries, are largely products of human-machine synergies. So, human chefs, food R&D teams, and product designers could achieve great feats by embracing the use of AI.
Whether you’re biting into a new snack or sipping the latest beverage trend, AI might just be the unseen chef behind it.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Babatunde Olufemi is a food scientist, educator, and science-based food writer with academic and practical exposure to food processing, nutrition, food safety, and the global food industry. Through Quill of Grubs, he breaks down complex food science topics into clear, accessible explanations for everyday readers, students, and professionals.