Experts and stakeholders in the global food system are trying to predict the future of lab-grown meat. However, what becomes of this new sustainable protein source depends on its adoption. Now, imagine yourself being offered two burger options at a fast-food restaurant. One burger is made with a frozen patty, and the other is made with meat grown in a lab. Which of the two will you go for?
The above scenario is not just hypothetical. Yes, you’re not likely to get served burgers containing lab-grown meat at a drive-in. However, the odds of that happening in a few years are imminent. The cultivated meat market will be thrown open to the public soon, as soon as it receives regulatory clearance.
In this piece, we will help you know what to expect from meat without animals. Similarly, this will serve as an update on lab-grown meat adoption and its potential benefits. Trust us not to leave out the challenges that are hovering around sustainable protein sources.
What Is Lab-Grown Meat and How Is It Made?
Lab-grown meat is a clean meat innovation that eliminates most of the bottlenecks of livestock farming. Unlike plant-based alternative protein sources, lab-grown meat is real meat, albeit grown in bioreactors by multiplying animal cells.
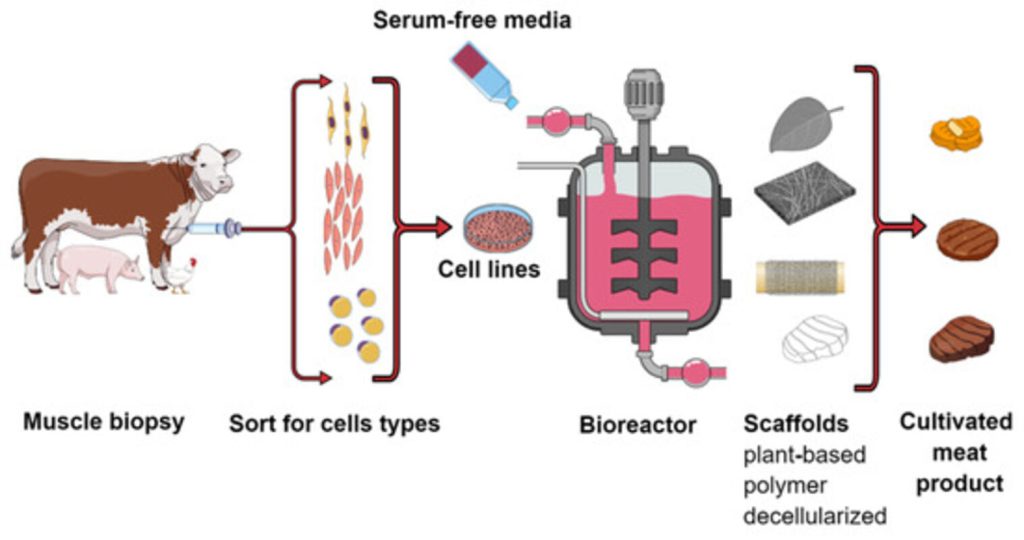
Growing meat in the lab eliminates the need for animal slaughter. Indeed, even the biopsy or collection of the animal cells to grow in the lab does no harm to the host animal. Even after a cow dies of natural causes, it is possible to have its cells still replicating in a bioreactor many years later. There, you have cell-cultured meat explained.
So, cultivating meat without animals to meet the global demand for protein becomes a win for all parties concerned.
ALSO READ: Lab-Grown Meat: Will We Be Eating It in the Next 10 Years?
Why the Buzz? Potential Benefits Explained
It is time to narrow down on the benefits of lab-grown meat as the future of food technology. We shall condense the benefits of a cell-based meat future into three sections below:
1. Health Control
To check disease-related reduction of livestock output, most farms rely heavily on antibiotics. Health advocates have raised an alarm about the recent proliferation of antimicrobial resistance in humans. Public health experts have traced the inordinate ingestion of antibiotics to industrially raised livestock products. The future of lab-grown meat promises the elimination of the antibiotics hurdle in products from animal sources.
In addition, meat without animals makes it possible to control the fat content of each meat serving. This fat proportioning is often done during the 3-D printing of the animal cells into meat tissues.

2. Ethical Appeal
So far, no ethical objections have been raised to the methods of producing lab-grown meat. The widespread adoption of lab-grown meat in the future may even eliminate the need to slaughter millions of animals annually.
There are even considerations of using lab-grown meats in kosher dishes. The only caveat is that the biopsy, or parent cell extraction, needs to be conducted on a kosher animal. National Geographic’s explainer on lab-grown meat has a bit more to say about public reaction to its acclaimed ethics.
3. Reduced Environmental Footprint
Livestock production has been fingered as one of the major contributors to global greenhouse gas emissions. So, the future of lab-grown meat will naturally resonate with planet-friendly food innovations and ethics.
The benefits of cell-cultured meat explained reveal that cutting back on conventional livestock farming activities, reduces climate impacts. In addition, promoting the adoption of lab-grown meat should reduce pollution of land and natural waterways.
Current Global Landscape
In December 2020, the Singapore Food Agency (SFA) took the bold step of approving bite-sized lab-grown chicken pieces. This made Singapore the first country to make lab-grown meat commercially available to its populace.
The US followed in quick stride in 2023. The Department of Agriculture (USDA) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) gave two companies the green light to make their lab-grown chicken available to the public.
Good Meat and Upside Foods are the two startups approved to sell cell-cultured meat in the United States. Several other companies are making giant strides in developing viable lab-grown meat products. Examples are Mosa Meat, Aleph Farms, and Eat Just.
Breakthroughs in food innovation and the ethics of cell-cultured meat are not limited to the United States and Singapore alone. Japan, the Netherlands and Israel are the countries leading in the number of R&D labs ideating on lab-grown meat products.
Market, Price, and Scale Challenges
Pricing and scaling are some likely bottlenecks that will self-resolve in the future of lab-grown meat startups. The disparity in kilo-per-kilo price of lab-grown meat relative to their conventional variants is very wide. While the cost of cell-cultured meat is steadily falling, it remains relatively expensive.
Venture capitalists may play a significant role in the future of food technology, particularly in the lab-grown burger market. Setting up bio reactor facilities for cultivating cell-based meat is capital-intensive. Also, after a viable product has been developed, making the product commercially available will cost even more money.

Investors are seldom driven by passion for innovation, but maximal returns make them tick. So, VCs may pressure cell-cultured startups into pushing lab-grown products too early.
In addition, cell-cultured meat startups will have to develop a distribution and logistics system for mainstream markets, all from scratch. Imagine a start-up having to supply the lab-grown burger market for restaurants across all the states in the US.
Consumer Acceptance and Cultural Barriers
There’s a lingering stigma about cultured meat being ‘unnatural.’ It’s so bad that some folks would not even try out cell-cultured meat before dismissing it as subpar. Yes, regulatory bodies are giving lab-grown meat safety clearances in countries like Singapore. However, cultural and religious reservations may still hamper its full adoption.

Seeing these impending human-centered hurdles, regulatory bodies may have to insist on transparency in the labeling of lab-grown meat. Companies looking to cash in on the global sustainable protein sources lab-grown burger market may not need to worry about marketing. Instead, they would need to prioritize sensitization and consumer education on the benefits of cell-cultured meat.
ALSO READ: The Environmental Impact of Food Delivery Services: What Convenience Is Costing the Planet
The Road Ahead: What’s Next for Cultivated Meat?
Cultivated meat is still in its first phase of commercial iteration. The future of lab-grown meat may eventually morph into multiple variants of the product. For example, just as hybrid cars are helping car users into the realities of EV technology, similar blends may play out with protein sources. In the future, you may find hybrid meat products, like regular meat and cultivated meat, or a blend of cell-based and plant-based meats. The global outlook on cultivated meat markets will require an international harmonization of regulations.
Some years ago, lab-grown meat was a speculative concept. Today, it is a reality and could become the leading protein source of the future. However, from the analysis in this piece, there’s more to the commercial and future success of cultivated meat than its sustainable benefits. Public trust, economics, policy and science will determine the future of lab-grown meat.
As the world looks for sustainable solutions, lab-grown meat may be a key ingredient in feeding the future.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Babatunde Olufemi is a food scientist, educator, and science-based food writer with academic and practical exposure to food processing, nutrition, food safety, and the global food industry. Through Quill of Grubs, he breaks down complex food science topics into clear, accessible explanations for everyday readers, students, and professionals.











